Who We Are
At Brego Business, our team of 200+ seasoned experts in , marketing, and finance is committed to one goal: driving your business forward.
We specialize in delivering seamless marketing and finance solutions. With over 1200+ success stories, from startups like Haptik to giants like Tata Projects, we deliver outcomes that matter.
By combining human expertise, technology, and proven strategies, we help businesses scale and thrive.
What We Do
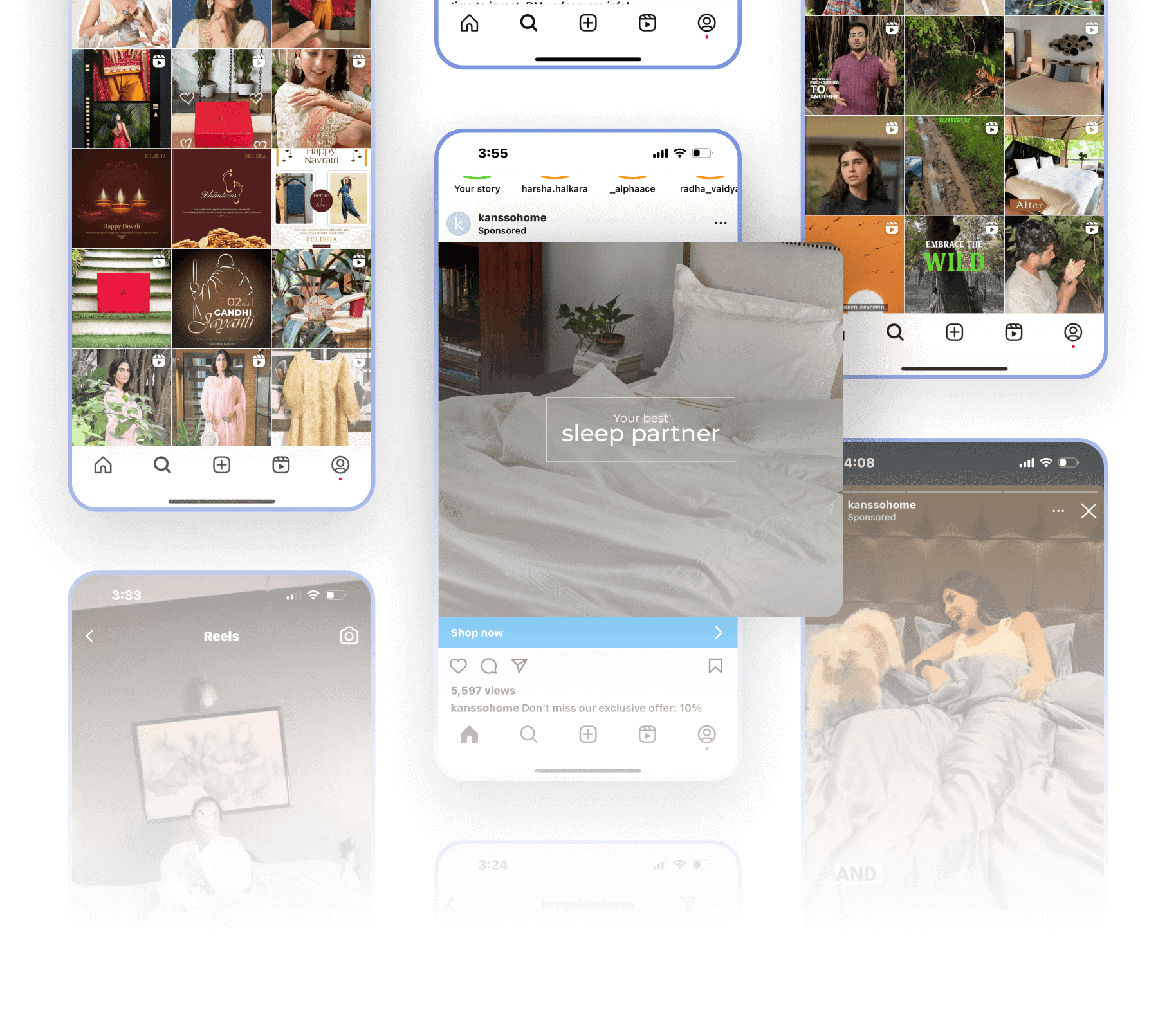
Marketing
Boost Sales. Build Impact.
We create content & craft campaigns that drive results, turning ideas into revenue. From strategy to execution, we ensure your brand gets noticed and your business grows.

Finance
Streamline Finances. Maximize Value
We streamline finances and deliver insights that drive growth. From bookkeeping to virtual CFO services, we ensure clean, compliant, and goal-aligned finances.
Who We Work With
Startups
We help entrepreneurs turn ideas into multimillion-dollar ventures by navigating funding, scaling operations, and finding market fit.
Family Business
We modernise family-run businesses while preserving their legacy, driving innovation, cutting costs, and staying competitive.
Enterprises
We enable enterprises to scale globally with tailored strategies that balance local insights and global growth goals.
Why We’re Different
Tech Forward
01
A dedicated team of domain experts that leverage existing technology to drive efficiency for your business.
The result, a seamless blend of humans and technology that comes together to drive results
Deep expertise
02
The result, a seamless blend of humans and technology that comes together to drive results
Our commitment extends to both emerging startups and well-established corporations, assuring that we adapt to your evolving requirements seamlessly
Scalable
03
We’re the last services firm you’ll ever need to hire.
Our commitment extends to both emerging startups and well-established corporations, assuring that we adapt to your evolving requirements seamlessly





































